Dry machining
Dry machining
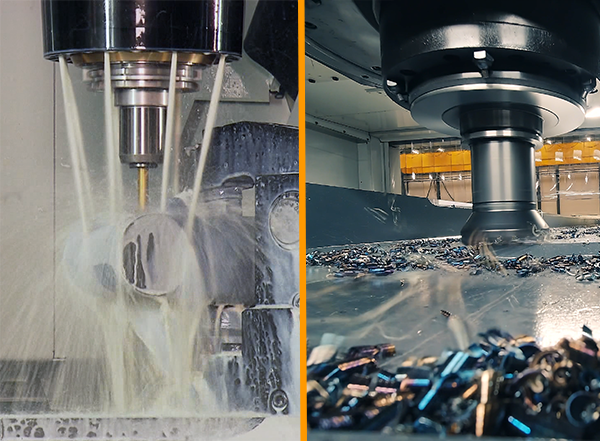
Dry machining is a machining process in which no coolant or lubricants are used during the cutting, milling, turning, or drilling of metal. Instead of liquid coolants such as oils or emulsions, dry machining often employs air cooling or minimal quantity lubrication (MQL). This means that a small amount of lubricant or air spray is applied to lubricate and cool the cutting tool and workpiece.
Advantages
- Lower operational costs: Dry machining eliminates the need for coolant, resulting in reduced expenses for purchasing, storing, and disposing of these fluids.
- Environmentally friendly: Dry machining reduces the use of chemicals, potentially lowering its environmental impact.
- Dry machining does not produce wastewater or harmful fumes that can harm the environment.
- Reduced maintenance: The absence of coolant means less machine maintenance, as there is no buildup of dirt and sludge that can disrupt equipment operation.
- Improved visibility: Dry machining enhances workpiece visibility, allowing operators to more easily detect issues and monitor work quality.
- No cleaning or degreasing: Because no coolants or lubricants come into contact with the workpiece, there is little to no need for post-machining cleaning or degreasing.
Disadvantages
- Higher temperatures: Dry machining can lead to elevated temperatures in both the workpiece and the tool, potentially shortening tool life and affecting dimensional and geometric stability.
- Increased tool wear: Dry machining may result in increased wear on cutting tools and workpieces, negatively impacting tool lifespan.
- Limited heat dissipation: Coolants also serve as heat dissipation agents. Dry machining can generate more heat, potentially reducing tool life and diminishing precision.
- Risk of burr formation: Dry machining can increase the risk of burr formation, necessitating additional post-processing and higher costs.
- Limitations for certain materials: Dry machining is not suitable for all materials, such as heat-resistant alloys.